What does a neuron look like? Biology Questions
Neurons (also known as neurones and nerve cells) are electrically excitable cells in the nervous system that process and transmit information. In vertebrate animals, neurons are the core components of the brain, spinal cord and peripheral nerves. Image:Complete neuron cell diagram.svg In some countries this may not be legally possible; if so:
Neuron Study Guide Inspirit Learning Inc
Neuron. Within a nervous system, a neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network. Neurons communicate with other cells via synapses, which are specialized connections that commonly use minute amounts of chemical neurotransmitters to pass the electric.
neuron diagram labeled
Choose the correct names for the parts of the neuron. (6) This neuron part receives messages from other neurons. (7) This neuron part sends on messages to other neurons. (8) This neuron part gives messages to muscle tissue. (9) This neuron part processes incoming messages. (10) This neuron part contains instructions for making proteins that the.

What Is a Neuron? Diagrams, Types, Function, and More
Neuron under Microscope with Labeled Diagram 25/04/2023 31/03/2022 by anatomylearner The structural and functional unit of the nervous system is the neuron that may easily observe under a light microscope. Neurons may vary considerably in size, shape, and other features.
Histology of the Nervous System (The Neuron) Part 1
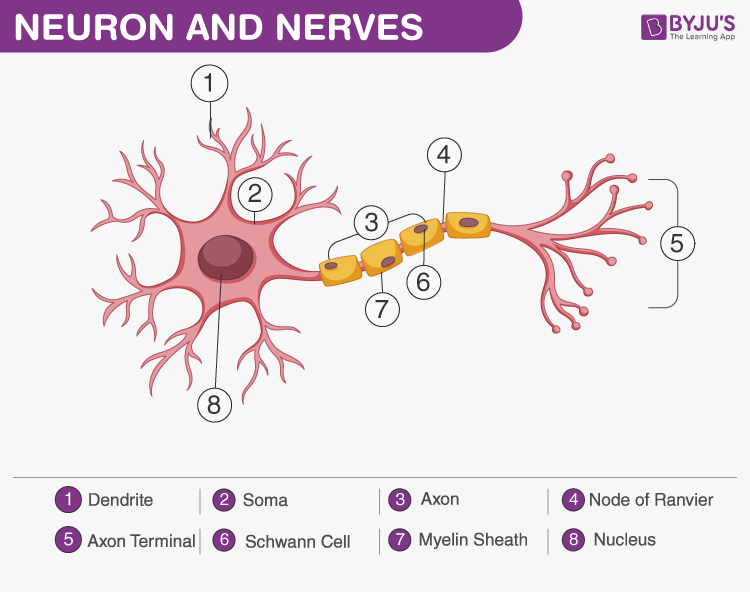
A Labelled Diagram Of Neuron with Detailed Explanations Biology Biology Article Diagram Of Neuron Diagram Of Neuron A neuron is a specialized cell, primarily involved in transmitting information through electrical and chemical signals. They are found in the brain, spinal cord and the peripheral nerves. A neuron is also known as the nerve cell.
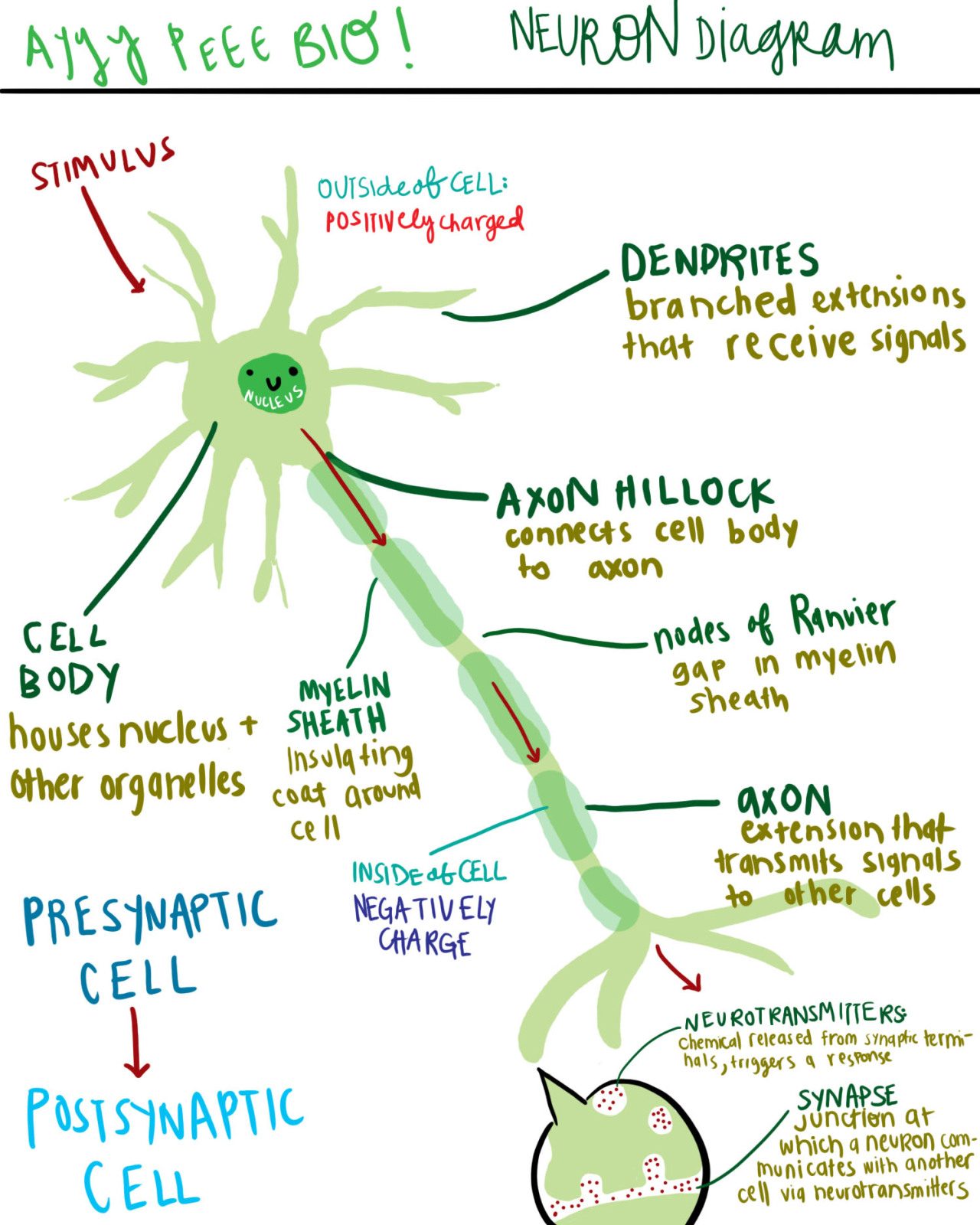
A diagram of a neuron and its functions. a study in chartreuse
At the synapse, the firing of an action potential in one neuron—the presynaptic, or sending, neuron—causes the transmission of a signal to another neuron—the postsynaptic, or receiving, neuron—making the postsynaptic neuron either more or less likely to fire its own action potential.

The Nervous System (Structure and Function) (Nursing) Part 1
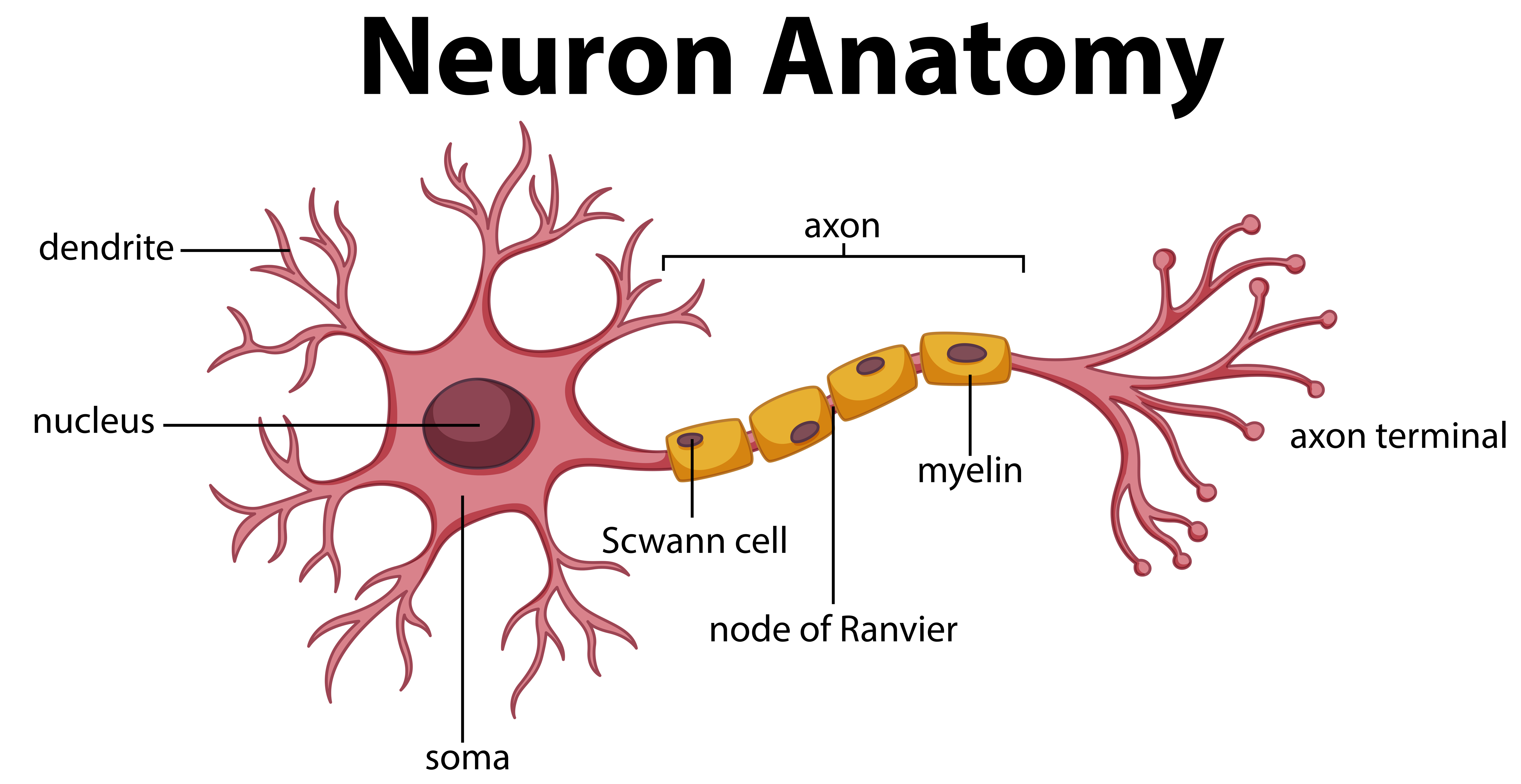
neuron, basic cell of the nervous system in vertebrates and most invertebrates from the level of the cnidarians (e.g., corals, jellyfish) upward.A typical neuron has a cell body containing a nucleus and two or more long fibres. Impulses are carried along one or more of these fibres, called dendrites, to the cell body; in higher nervous systems, only one fibre, the axon, carries the impulse.

Figure 7 4 Structure Of A Typical Motor Neuron Bangmuin Image Josh
How do you know where you are right now? Your ability to perceive your surroundings - to see, hear, and smell what's around you - depends on your nervous system. So does your ability to recognize where you are and to remember if you've been there before.
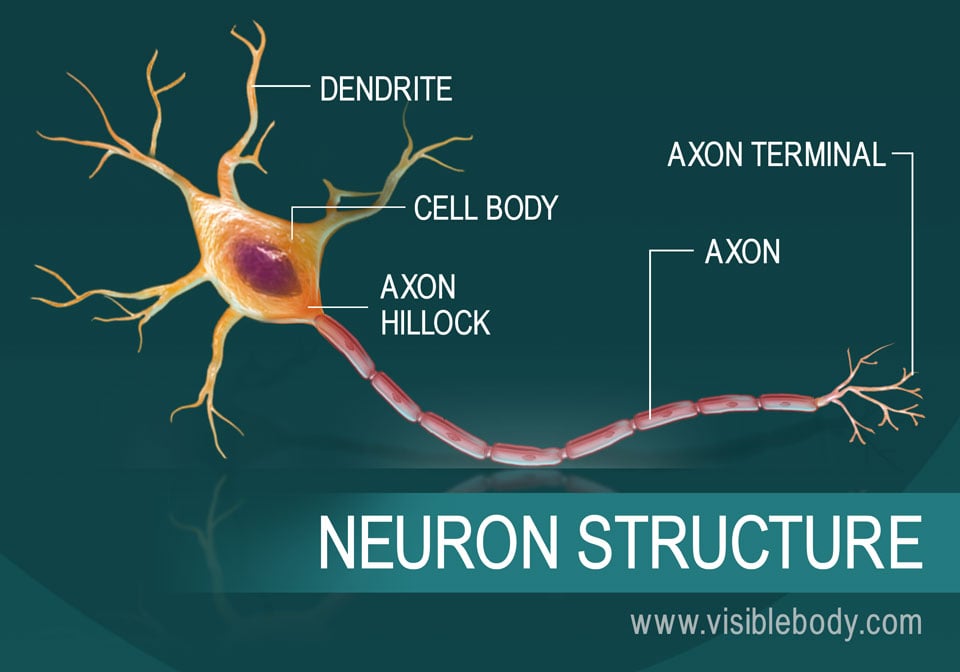
Neurons
A neuron consists of neurotransmitters in the synaptic vesicles of the terminal buttons; it releases chemicals that travel across a synapse and conduct signals from one neuron to another one. Ques. Draw a labelled diagram of the neuron. (2 marks) Ans. Ques. What are receptors and what are the classification of receptors? (2 marks)
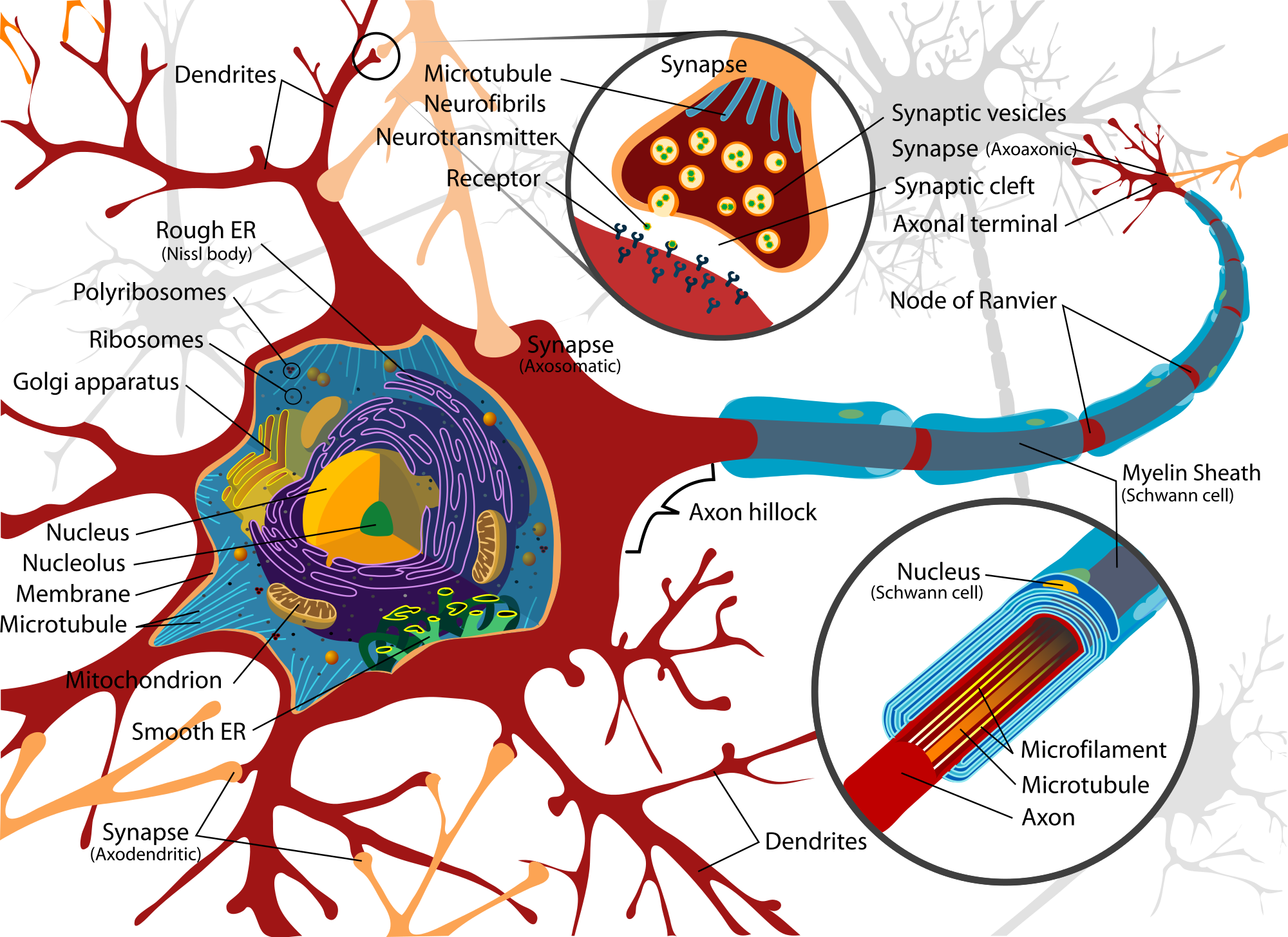
Nerve Cell Diagram Labeled ClipArt Best
Nervous tissue is composed of two types of cells, neurons and glial cells. Neurons are the primary type of cell that most anyone associates with the nervous system. They are responsible for the computation and communication that the nervous system provides. They are electrically active and release chemical signals to target cells.

FileNeuron1.jpg Simple English Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Labeled Diagram of a Neuron Definition of Neuron The building blocks of the system responsible for transmitting and processing information are called neurons. What are Neurons? Neurons are specialised cells that plays an important role in facilitating communication among different parts of our body.
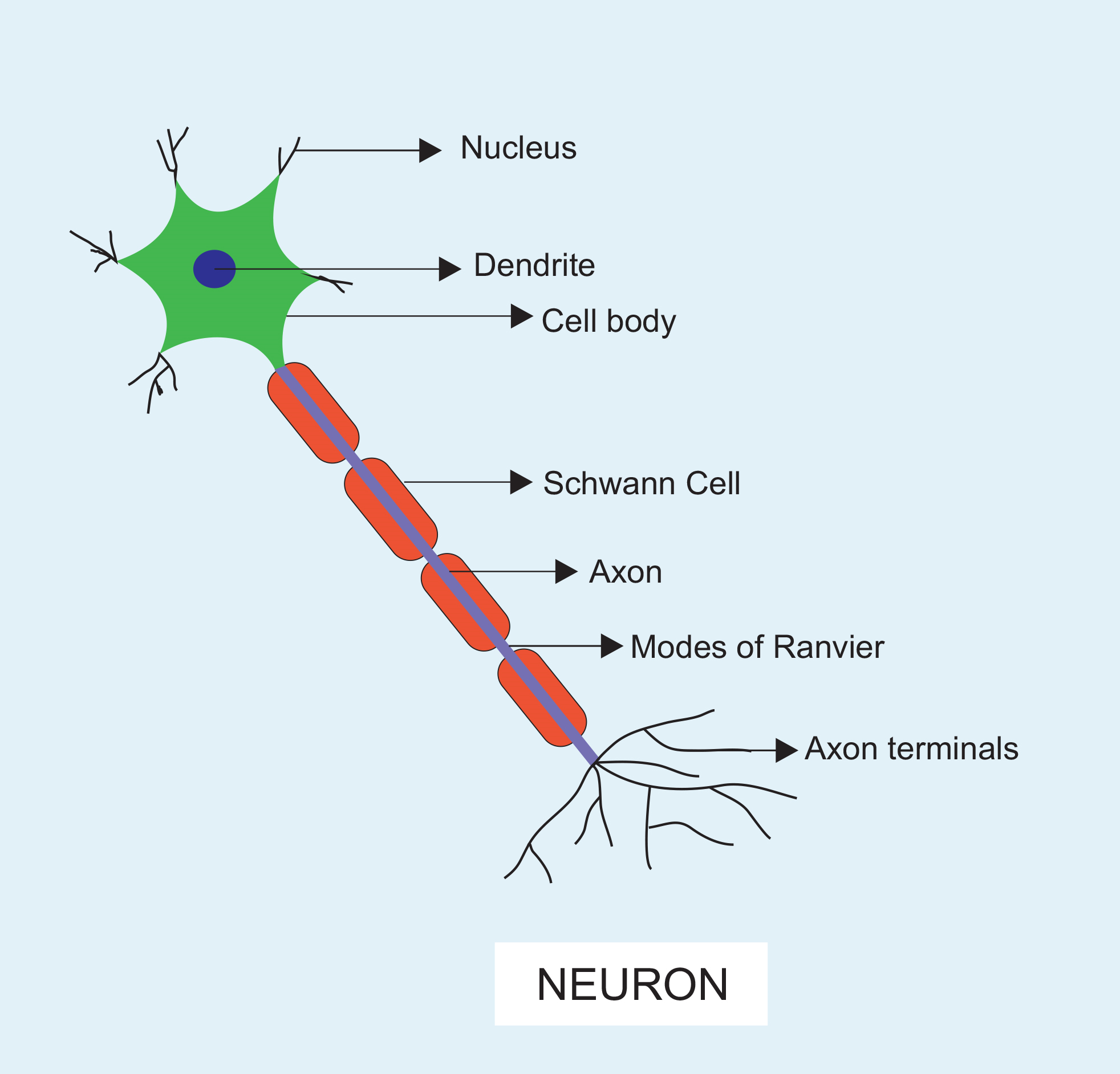
What does a neuron look like?
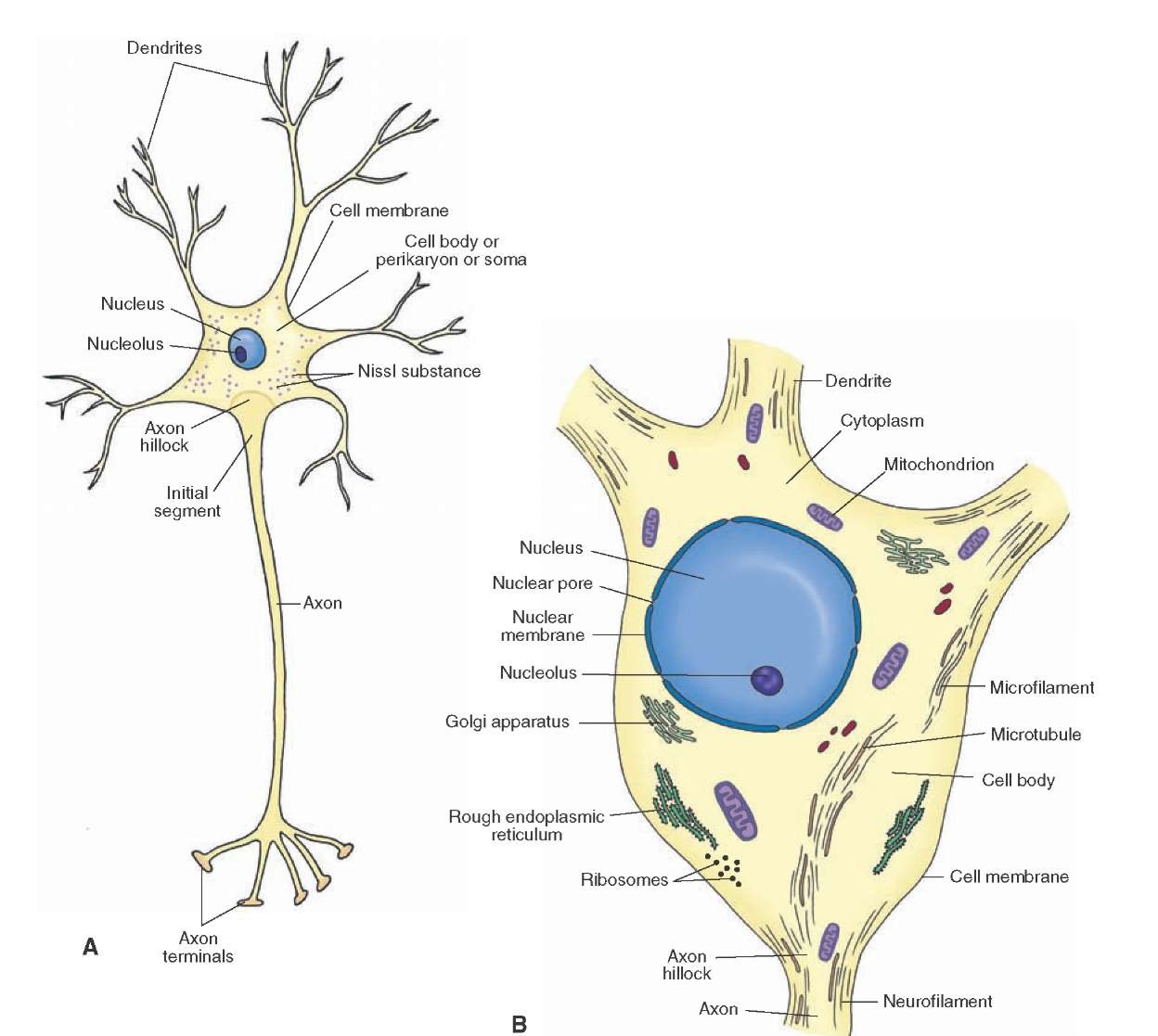
The cell body of a neuron, also known as the soma, is typically located at the center of the dendritic tree in multipolar neurons.It is spherical or polygonal in shape and relatively small, making up one-tenth of the total cell volume.. The functionality of the neuron is highly dependent on its cell body as it houses the nucleus, which contains the genetic material (DNA) of the cell as well as.
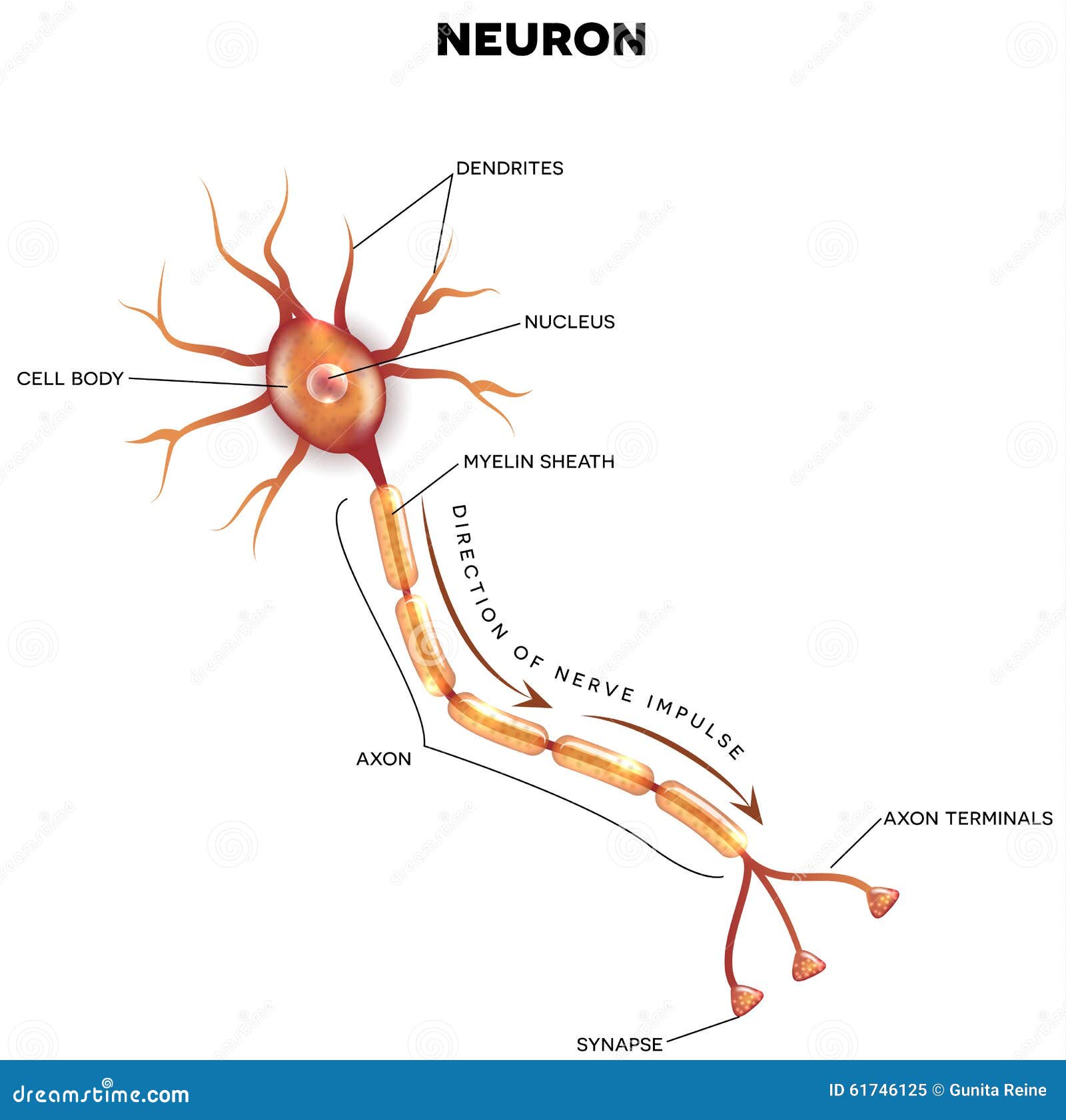
Labeled Diagram of the Neuron Stock Vector Illustration of anatomical
What is a Neuron? Neurons are the building blocks of the nervous system. They receive and transmit signals to different parts of the body. This is carried out in both physical and electrical forms. There are several different types of neurons that facilitate the transmission of information. 6,435
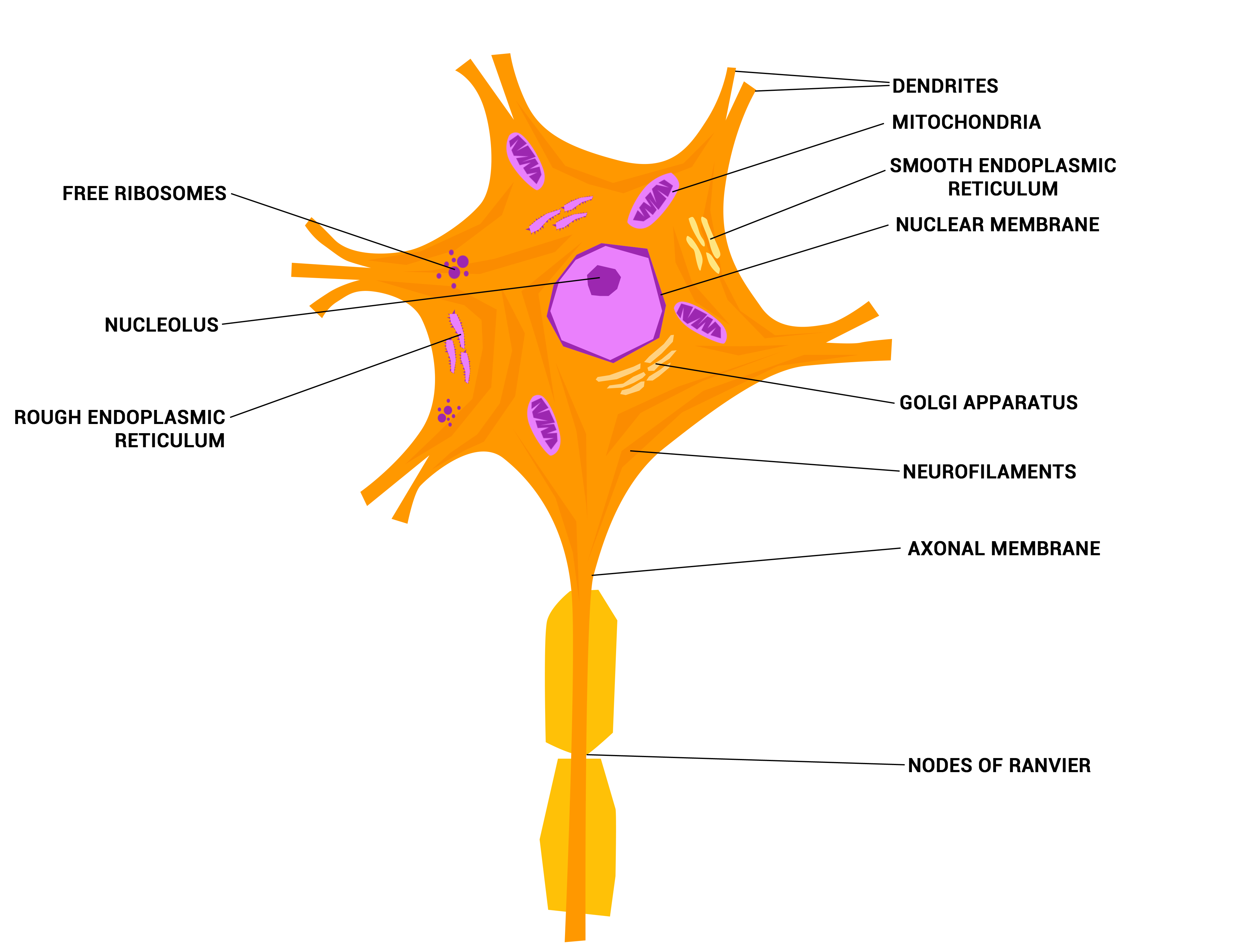
Neurons The crazy wires in our body. Doc Jana
A neuron (nerve cell) is a specialized cell that conveys electrochemical impulses throughout the body. The cytology of a neuron facilitates the transmission of either: 'top-down' information from the brain to the periphery, via efferent neurons (e.g. to permit locomotion) (efferent neurons) or,

Anatomy Of A Neuron ANATOMY
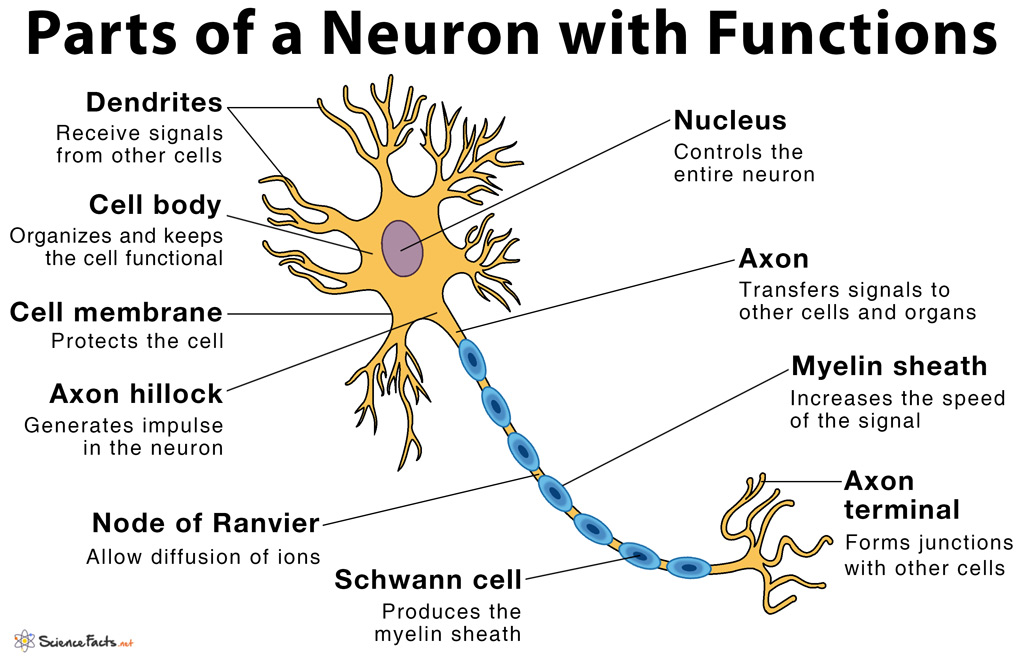
Neuron Anatomy Nerve Cell: Dendrites receive messages from other neurons. The message then moves through the axon to the other end of the neuron, then to the tips of the axon and then into the space between neurons. From there the message can move to the next neuron. Neurons pass messages to each other using a special type of electrical signal.
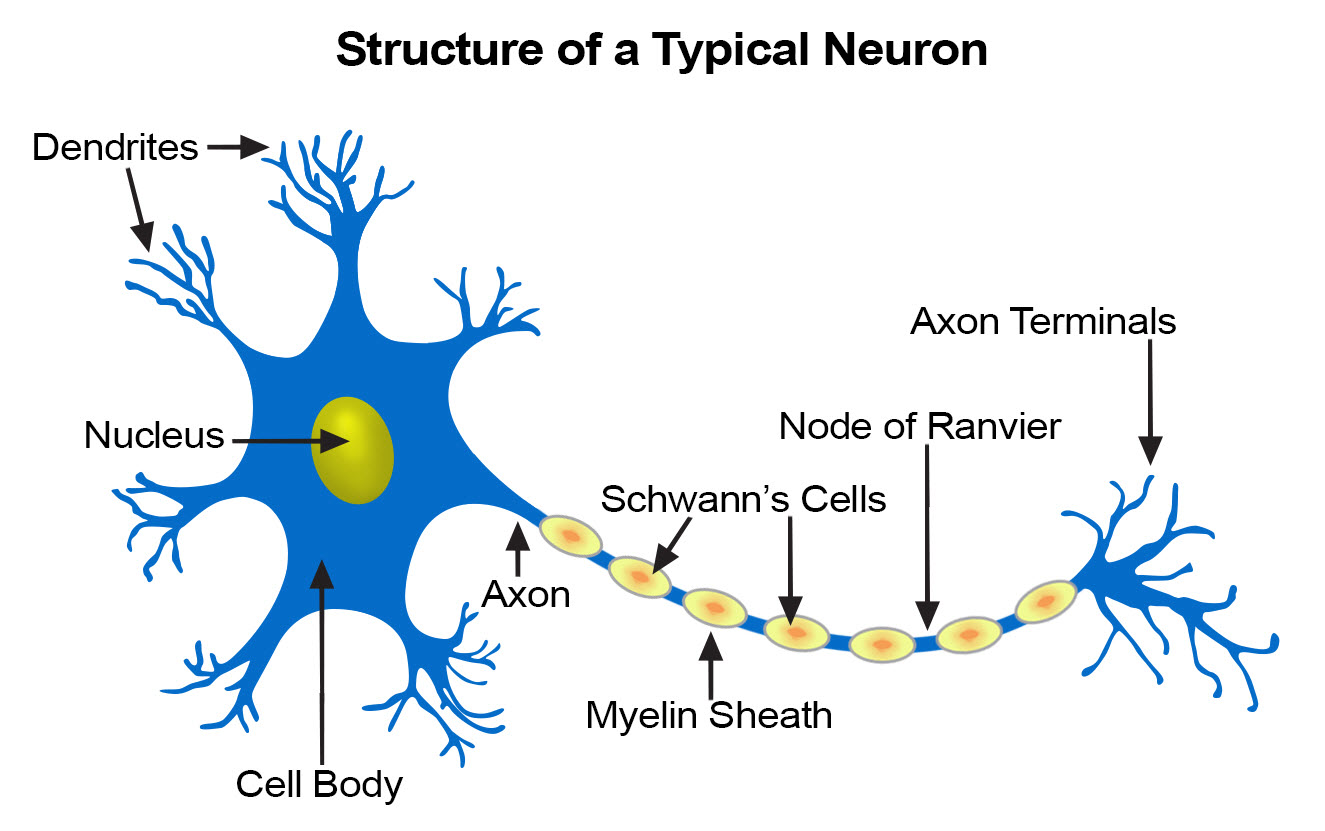
Nerve Tissue SEER Training
The nervous system is a network of neurons whose main feature is to generate, modulate and transmit information between all the different parts of the human body. This property enables many important functions of the nervous system, such as regulation of vital body functions ( heartbeat, breathing, digestion), sensation and body movements.